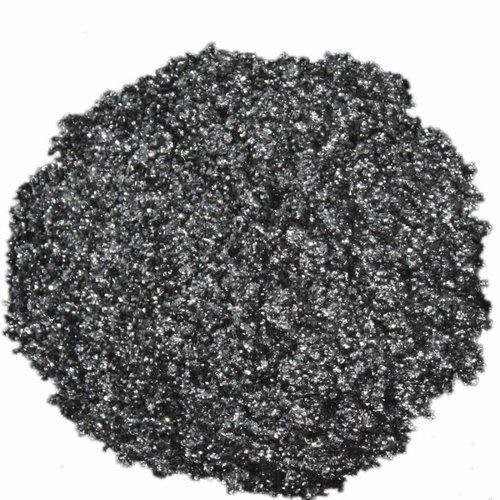
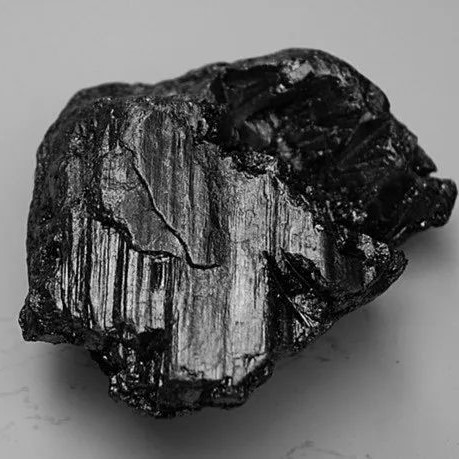
Natural Flake Graphite
Natural Graphite results from the transformation of organic matter deposits subjected to the effect of very strong metamorphic pressures combined with high temperature, over millions of years. Basically, the graphite flakes are liberated by successive phases of mechanical grinding in wet phase. The purpose of this stage is to release the maximum of graphite flakes while trying as well as possible to preserve the integrity of the large-sized flakes. Subsequently, the flakes released are separated from the impurities (gangue) by flotation. This process, repeated several times, makes it possible to reach purity levels of carbon.
Natural Flake Graphite is also called natural crystalline graphite. Its shape resembles fish scale, so it is called flake graphite. It belongs to the hexagonal crystal system and has a layered structure.
Known for its high degree of macro-crystallinity, flake graphite’s high thermal and electrical conductivity, low spring-back properties , thermal shock resistance and corrosion resistance make it excellent in molding, friction, and conductive applications. It is also a choice material for powder metallurgy, batteries, fuel cells, refractories, general lubricants, rubber compounds, pencils, gaskets, and polymer systems.
| Material | |
|---|---|
| Specifications | Natural Flake Graphite FC- 99% |
| FC | 99% min |
| Ash | 0.50% max |
| Moisture | 0.15% max |
| Size | +80 mesh -80% min -80 mesh - 20% max |